The Government of Ontario, through the Ministry of Energy and Mines, sets the overall policy for the energy sector. It does this mainly through laws and regulations.
The Ontario Energy Board regulates Ontario’s energy sector. We ensure that natural gas and electricity companies follow the rules. As an independent government agency, our goal is to promote a sustainable, reliable energy sector that helps consumers get value from their natural gas and electricity services. Learn more about our mission and mandate.
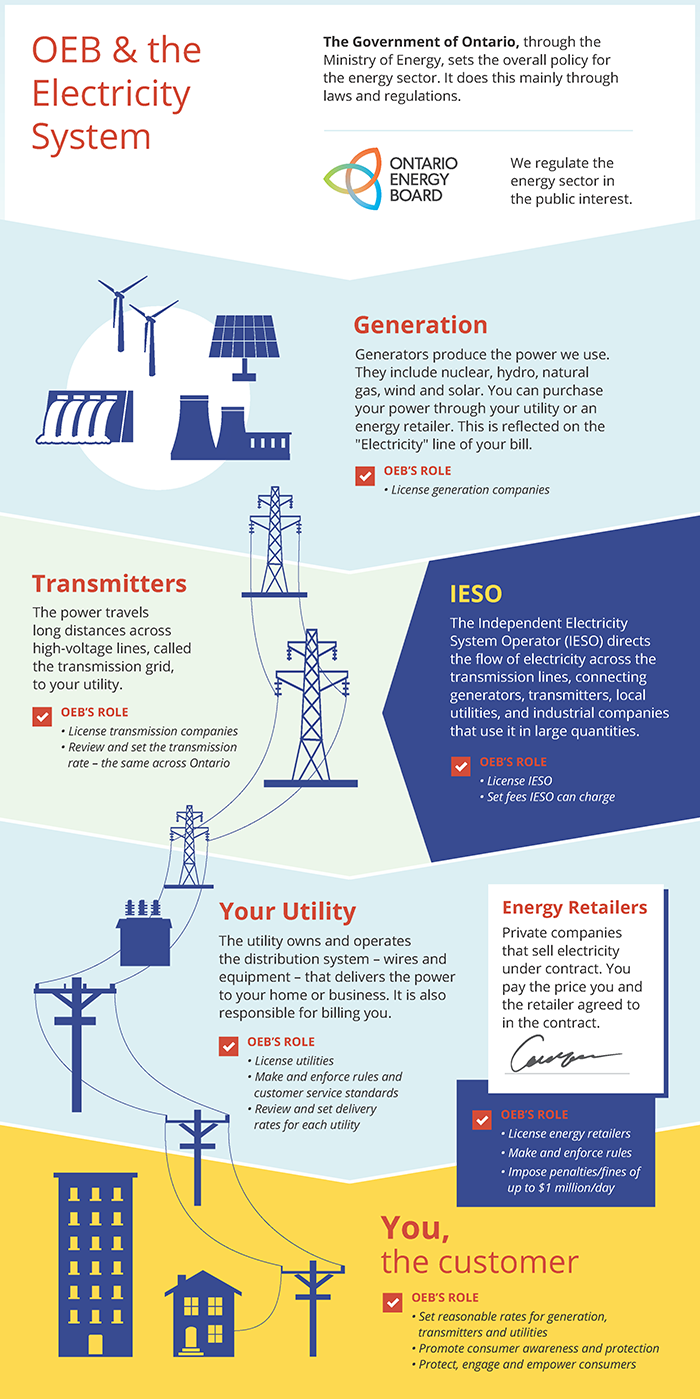
The electricity sector
Different companies and agencies play a part in ensuring that Ontario’s homes and businesses have a reliable supply of electricity when they need it, including:
Generators
Generation companies produce the electricity we use. They include facilities powered by nuclear, hydro, natural gas, wind and solar sources. The largest generator is Ontario Power Generation – a provincially-owned company. This is how the generation mix looks in Ontario today:
Transmitters
Once electricity is generated, it travels across Ontario on high-voltage transmission lines. These lines, which are mostly owned and operated by Hydro One, take power from the generator to the doorsteps of local utilities. There, it is put through transformers that convert it to low-voltage power. It is then sent out on distribution lines.
Distributors
Local utilities (also known as distributors) own and operate the low-voltage lines that deliver power to your home or business. They are also responsible for billing you and delivering conservation programs.
See the electricity utility performance dashboards for more information about your local utility
Retailers
You have choices about who to buy your electricity from. The vast majority (about 95%) of Ontarians choose to buy electricity from their local utility. If you do nothing, you automatically buy electricity from your local utility, and your electricity rates are set by the Ontario Energy Board. We do not allow utilities to profit from the sale of electricity.
However, if you choose to buy electricity from a private company that sells electricity under contract (called an electricity retailer), you pay the price that you and the retailer agree to in the contract. There are a number of electricity retailers offering electricity contracts to consumers across Ontario. See a list of licensed electricity retailers that are active in Ontario.
No matter who you buy your electricity from, it is delivered to your home or business through the same wires.
The Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO)
The IESO balances the supply of and demand for electricity in Ontario. It directs the flow of electricity across the province's transmission lines, connecting generators that produce power, transmitters that send it across the province, local utilities that deliver it to people’s homes and businesses, and industrial companies that use it in large quantities. The IESO plans the power system and makes sure Ontario has enough electricity over the long term. It also coordinates conservation efforts across the province.
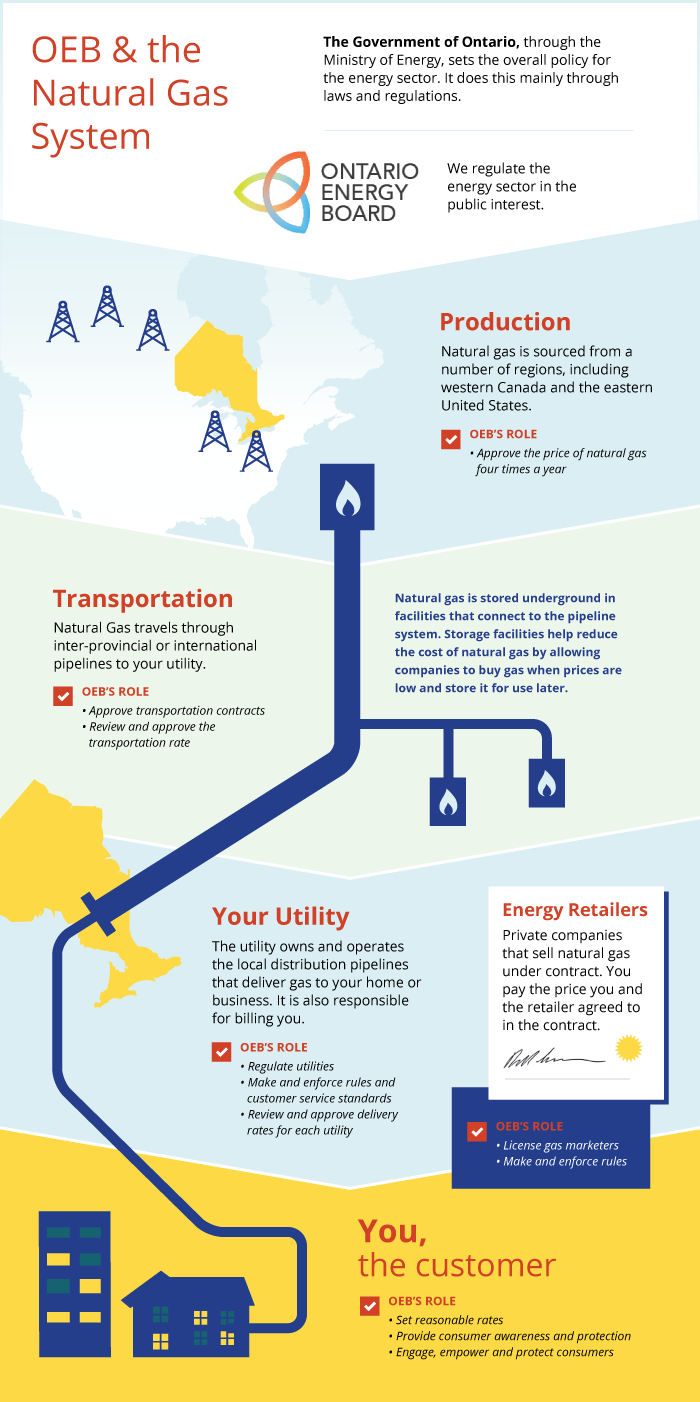
The natural gas sector
Several different companies play a part in providing a reliable supply of natural gas to Ontario homes and businesses.
Producers
Producers are companies that look for, produce or process natural gas. Most of the natural gas used in Ontario comes from Alberta.
Transmitters and storage companies
Natural gas flows to Ontario from Western Canada and the United States through large high pressure transmission pipelines like the Trans Canada Pipeline that connect to the smaller low pressure pipelines owned by local utilities. Natural gas is stored underground in facilities that connect to the pipeline system. Natural gas distributors often own storage facilities. Storage facilities help reduce the cost of natural gas by allowing companies to buy gas when prices are low and store it for use later.
Distributors
Distributors, also known as utilities, own the pipes and equipment that deliver natural gas to your home or business. There are only a handful of major gas utilities in Ontario. We regulate the rates for two of them: Enbridge Gas Inc.and EPCOR Natural Gas Limited Partnership.
Natural gas marketers
You have choices about who to buy natural gas from. The vast majority (about 95%) of Ontarians choose to buy natural gas from their utility. If you do nothing, you automatically buy natural gas from your utility, and the rates are approved by the Ontario Energy Board if you are served by Enbridge or EPCOR. We do not allow utilities to make a profit from the sale of natural gas.
If you choose to buy your natural gas from a private company that sells natural gas under contract (called a natural gas marketer), you pay the price that you and the natural gas marketer agree to in the contract. There are a number of natural gas marketers offering natural gas contracts to consumers across Ontario. See a list of licensed natural gas marketers that are active in Ontario.
No matter who you buy your natural gas from, it is always delivered to you by your utility.